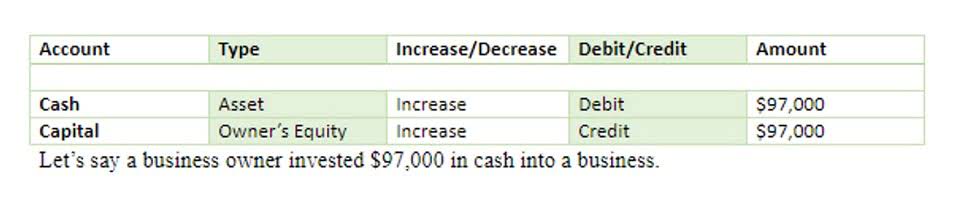
User groups consist of those most interested in or affected by accounting rules. Some accountants have said that politicization in the development and acceptance of generally accepted accounting principles (i.e., rule-making) is taking place. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles were eventually established in response to the 1929 Stock Market Crash and the Great Depression it caused. Many contribution margin experts believed that the great depression resulted from some publicly-traded companies’ unregulated and non-standardized financial reporting practices. Users expect these statements to present the company’s financial operations fairly, completely, and clearly.
Accounting Constraints According to GAAP
She’s excited to share her delicious cupcakes with the community, and she wants to track her expenses to ensure her business is profitable. However, Lucy is unfamiliar with GAAP and doesn’t strictly follow its guidelines when recording her financial transactions. GAAP plays a crucial role in maintaining transparency and integrity in the financial world.
Additional Guidelines
- For example, employee wages should be documented in the week they performed work, not the week when they actually receive their paycheck.
- In addition to these entities, GAAP is also regulated by the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC), which is a comprehensive source of GAAP guidance.
- GAAP, or Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, is a set of standards and guidelines that dictate how financial statements should be prepared and presented.
- GAAP includes certain revenue recognition standards that companies must follow to ensure that revenue is recognized when a sale has been transacted, regardless of when the customer pays.
- GAAP must always be followed by accountants and businesses when handling financial information.
- The rules set forth in GAAP improve consistency and clarity of financial communication by ensuring that all public U.S. companies report their financial status in either identical or very similar manners.
This principle is especially important because it ensures that users and readers of the financial statements are not misled by a lack of information. This is one of the most fundamental yet sometimes overlooked accounting concepts. Small-business owners should keep their business finances separate from personal ones. If you own more than one business, you should keep separate financial records for each company—doing so will give you an accurate view of how your business is doing. The United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) was created as a result of the Great Depression. The SEC encouraged the establishment of private standard-setting bodies through the AICPA and later the FASB, believing that the private sector had the proper knowledge, resources, and talents.
Depreciation and GAAP

While non-publicly traded Insurance Accounting companies aren’t required to follow GAAP, it is still highly regarded by lenders and creditors. Most financial institutions require annual GAAP-compliant financial statements as a part of their debt covenants when issuing business loans, leading many U.S. companies to adopt GAAP. Essentially, this principle requires accountants to report financial information only in the relevant accounting period.
- Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)a is the accounting standard adopted by the U.S.
- The accrual method provides an accurate, real-time view of a company’s finances and cash flow, allowing it to plan for the future and manage its debts and obligations.
- These principles were determined by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
- GAAP combines authoritative standards set by policy boards and widely accepted methods for recording and reporting accounting information.
- In 1939, urged by the SEC, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) appointed the Committee on Accounting Procedure (CAP).
- The cost becomes the basis for the accounts during the acquisition and subsequent accounting periods.
If a company is found violating GAAP principles, there are many possible consequences. Answering commonly asked questions about the generally accepted accounting principles. Using the best accounting software can make abiding by GAAP standards a bit easier. Some big names, like QuickBooks, are ones that small businesses frequently turn to.
- To help you understand the mission of GAAP’s standards and rules, let’s dive into the four main principles you need to know.
- The time interval must be identified on the heading of the company’s financial statements.
- This includes how to recognize premiums and claims, how to calculate reserves, and how to account for reinsurance.
- Accounting principles help hold a company’s financial reporting to clear and regulated standards.
- GAAP requires companies to use fair value accounting for certain assets and liabilities.
- When compiling reports, accountants must assume a business will continue to operate.

If you believe your small business may eventually be subject to GAAP, you may wish to follow the standard as early as possible. If it’s within your budget, your company can retain the services of an experienced finance lawyer accounting definition to assist you in vetting accountant candidates during the interview process. This professional can assist you in asking questions to determine your applicant’s level of familiarity with GAAP.
Time period principle

Cash flow is life for a small business, so protect yours with the best possible accounting practices. This requires accountants to use the same financial reporting methods across all financial statements for easier comparisons of one financial statement to another. GAAP covers a wide range of accounting topics, including revenue recognition, inventory valuation, and depreciation.

Without GAAP, investors might be more reluctant to trust the information presented to them by public companies. Without that trust, fewer transactions and higher transaction costs could result, ultimately weakening the economy. GAAP also helps investors analyze companies by making it easier to perform „apples-to-apples” comparisons between one company and another, allowing for more accurate and consistent analysis. As global operations and markets expand, international standards like IFRS are gaining traction, even in the U.S. Nearly all S&P 500 companies report at least one non-GAAP measure in their financial statements. Investors should be cautious if a financial statement isn’t prepared using GAAP.

